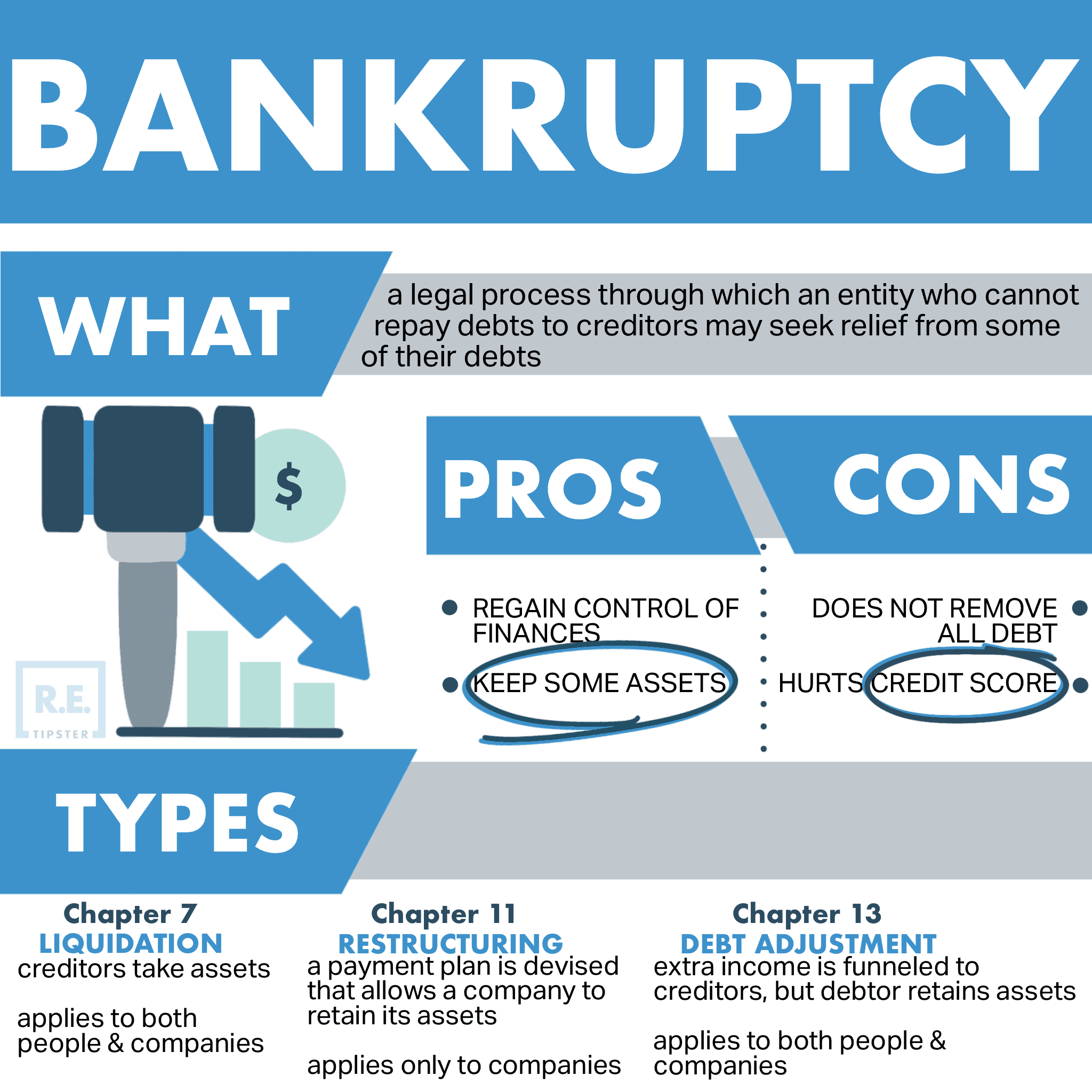
What is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
REtipster does not provide legal advice. The information in this article can be impacted by many unique variables. Always consult with a qualified legal professional before taking action.
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy Explained
Chapter 7 bankruptcy involves collecting all of a debtor’s assets, liquidating the assets into cash, and distributing the cash to the creditors based on the loan balances and type of debt owed to each creditor. When the bankruptcy proceeding is complete, the debtor is released from their debt obligations covered by the bankruptcy.
A Chapter 7 bankruptcy may be voluntarily chosen by the debtor (e.g. – in the event of a financial catastrophe, when the borrower is unable to meet their debt obligations) or it can be triggered against the borrower’s will (triggered by the lenders if the borrower falls into default).
In a Chapter 7 bankruptcy, the court appoints a trustee to carry out the liquidation of collateral and disburse the liquidated proceeds. In order to receive any of the liquidated proceeds, the lender must file a proof of claim to the court.
There is no additional repayment after the liquidated assets are disbursed among the creditors.
What Happens In A Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
Chapter 7 bankruptcy is commonly known as “liquidation bankruptcy” because as the name implies, it will liquidate your assets to pay off as much of your debt as possible. For example, if you own rental properties and can’t pay the mortgages on them, the court typically orders you to sell the properties and pay the proceeds to your lenders.
After you sell off all your assets, the court generally discharges any remaining debts. Unsecured debts, such as personal loans or medical debts, typically disappear after a Chapter 7 bankruptcy.
Borrowers may keep several exempt assets, even when filing a Chapter 7 bankruptcy. In most cases, the borrower can keep their primary residence and basic furniture, their car, their professional tools (if applicable), their retirement accounts such as a 401(k) and IRA, and a small amount of cash. The rules vary by state, however, so check on your state’s bankruptcy laws.
That said, you must be able to afford to continue making payments on your home and car loans if you are to keep them. A Chapter 7 bankruptcy doesn’t erase those debts — if you want to keep them, you must reaffirm those debts and your ability to pay them.
Borrowers must appear before their creditors, who can ask them questions about their assets, income, and other debts. The court-appointed trustee has ultimate decision-making power over what the borrower must sell, who they must repay, and the terms of any modified loans.
Ultimately, borrowers declare a Chapter 7 bankruptcy when they have far fewer assets than liabilities, so lenders tend to see only a fraction of the money they’re owed if anything. A Chapter 7 bankruptcy will remain on the borrowers’ credit reports for ten years, and they cannot file another Chapter 7 bankruptcy for at least eight years.
Reviewed by Mark H. Zietlow, Innovative Law Group
References
- ^ “Chapter 7 – Bankruptcy Basics.” uscourts.gov, www.uscourts.gov/services-forms/bankruptcy/bankruptcy-basics/chapter-7-bankruptcy-basics. Accessed 24 Mar. 2020.
- ^ Ruth, George E. Commercial Lending. 5th ed., Washington, D.C., American Bankers Association, 2004, pp. 305-06.





