What Is Revolving Credit?
REtipster does not provide tax, investment, or financial advice. Always seek the help of a licensed financial professional before taking action.
Shortcuts
- Revolving credit is a flexible borrowing method allowing access to funds up to a predetermined limit, to be repaid and borrowed again.
- Common forms of revolving credit include credit cards, home equity lines of credit (HELOC), and personal lines of credit.
- Revolving lines of credit offer numerous benefits like flexibility and access to emergency funds but pose risks like overspending and high interest rates.
- Revolving credit is a type of line of credit, but not all lines of credit can be revolving.
- In real estate investing, revolving credit can provide readily accessible funds for property purchases, renovations, and bridging income gaps.
How Revolving Credit Works
Revolving credit works like a cyclic loan. It gives borrowers a maximum credit limit from which they can borrow, repay, and borrow again.
For example, if you have a credit limit of $10,000 and borrow $2,000, you now have an outstanding loan balance of $2,000, with $8,000 left to use on the line of credit. Once you repay the $2,000, your available credit goes back to $10,000. Note that interest is charged only on the amount borrowed, not the entire credit limit[1].
This cycle can continue until the maturity date of the loan, providing the borrower with flexible access to funds as long as they meet their repayment obligations and stay within the credit limit. It’s a dynamic system that serves the financial needs of consumers, businesses, and investors alike, offering flexibility and on-demand access to funds.
However, revolving credit also demands more responsibility. The interest rates are often higher and variable[2], particularly on revolving lines of credit. Also, easy access to credit might tempt one to overspend, potentially leading to a debt cycle.
Keeping borrowing within manageable limits, making timely repayments, and keeping a close eye on the credit utilization ratio—the percentage of available credit you’re using—are key to maintaining financial health and minimizing negative impacts on your credit score.
Impact on Credit Score
Your revolving credit usage often has an impact on your credit score.
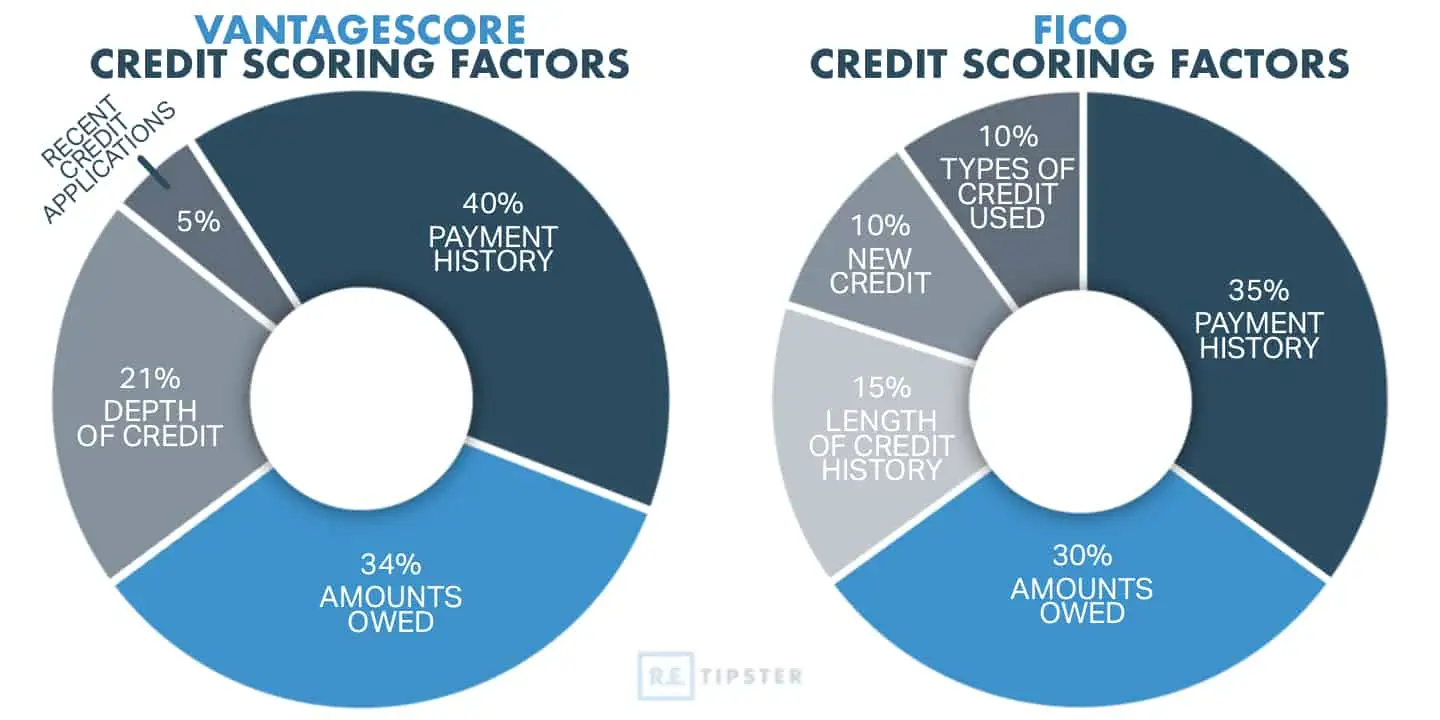
Credit utilization ratio is a major factor in calculating credit scores. A lower ratio, ideally below 30%[3], is generally better for your score. Lenders and investors pay close attention to this ratio as an indicator of your creditworthiness and financial management skills.
VantageScore and FICO weigh credit utilization differently (34% and 30%, respectively), but they occupy a significant chunk of your overall score.
Types of Revolving Credit
Revolving credit appears in several forms, the most common being credit cards. When you use a credit card, you’re borrowing against a credit limit and can pay back and borrow again.
A home equity line of credit (HELOC) is another. This involves borrowing against the equity in your home, giving you a line of credit you can draw from as needed.
Personal lines of credit operate similarly. They offer a set amount of funds you can draw from, and like the others, you only pay interest on what you borrow.
Revolving Line of Credit vs. Line of Credit
In its broadest sense, a line of credit is a credit arrangement that allows borrowers to draw funds up to a predetermined limit. Once these funds are repaid, they can be borrowed again.
However, not all lines of credit are revolving. Some are non-revolving, meaning that once the funds are repaid, the line of credit closes and cannot be used again[4].
On the other hand, revolving lines of credit are a specific type of credit that stays open even after the borrowed funds are repaid. These forms of credit provide continuous access to funds up to the agreed limit as long as the borrower meets the repayment obligations and doesn’t exceed the credit limit.
A revolving line of credit, also known as a “revolver,” is useful in cases where the exact amount of an upcoming expense may vary, such as renovation. A HELOC is an example of a revolving line of credit.
Revolving Credit and Its Uses
There are many ways to use revolving credit besides racking up consumer debt. Its many advantages include its flexibility, which is why it’s a convenient tool for financing investments and certain business operations.
Revolving Credit and Real Estate Investing
In real estate investing, particularly in land investing, investors can use revolving credit as bridge financing or to leverage their investment capacity, among other things.
Here are some specific scenarios where revolving credit is useful:
- Financing property purchases: Investors often use HELOCs as a source of low-interest funds. For example, if an investor identifies a promising property that’s undervalued or in a rapidly appreciating market, a HELOC can provide the necessary funds to act quickly[5]. This is especially useful in competitive markets where speed is paramount to securing the deal.
- Renovation and repair costs: Revolving credit can also help manage the unpredictability of renovation and repair costs. For instance, renovation costs can vary significantly[6] in a fix-and-flip scenario, and unforeseen issues can lead to unexpected expenses. Here, an investor may use a revolving line of credit to manage these costs efficiently without securing additional loans.
- Bridging income gaps: Revolving credit can also help bridge gaps between rental income and expenses for rental properties. If there’s a delay in rent payments or a vacancy period, a line of credit can cover mortgage payments, maintenance costs, or property taxes until rental income is restored. This provides landlords with financial stability and the ability to manage their properties effectively.
RELATED: How to Use a Home Equity Loan to Buy Another House
Revolving Credit and Small Businesses
Small businesses can take advantage of revolving credit in several ways.
Business credit cards and business lines of credit (BLoCs) are two common forms of revolving credit that can provide businesses the flexibility to manage their finances effectively.
Revolving credit can help small businesses manage short-term needs (such as payroll and operational expenses)[7] and seasonal variations in cash flow. It’s not uncommon for businesses to experience periods of low cash flow, followed by periods of higher income. Revolving credit can help bridge these gaps, ensuring the business can continue operating even during lean periods.
Business revolving credit can also be used for investment opportunities. For example, if a business opportunity presents itself and the business does not have enough cash on hand, it can use its revolving credit to seize the opportunity. This credit could be used to invest in new equipment, expand operations, or increase inventory.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Revolving Credit
Revolving credit, while a powerful financial tool, comes with both risks and benefits that users should be aware of.
Benefits
- Flexibility: Revolving credit allows for a flexible borrowing experience. It provides funds on demand up to a predefined limit, and you only pay interest on the amount you use. This flexibility can be especially helpful in managing irregular or unpredictable expenses.
- Emergency funds: Having access to revolving credit can provide peace of mind in case of emergencies or unexpected expenses. This ready source of funds can help manage financial shocks without needing to secure a new loan each time.
- Building credit history: Regular and responsible use of revolving credit can help build a positive credit history[8]. Lenders look favorably on borrowers who demonstrate they can manage credit responsibly.
Risks
- Potential for overspending: The easy access to credit might tempt some to spend beyond their means. This can lead to significant debt, especially considering the higher interest rates often associated with revolving credit.
- Higher interest rates: Compared to other forms of credit, revolving credit usually has higher interest rates[9]. Over time, these interest payments can add up, especially if you’re only making minimum payments.
- Impact on credit score: Your credit utilization ratio[10] plays a big role in your credit score calculation. High utilization can hurt your credit score.
Sources
- Rathner, S. (2022, June 2.) How to Avoid Credit Card Interest — or at Least Reduce It. NerdWallet. Retrieved from https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/credit-cards/how-to-avoid-credit-card-interest
- Bond, C. (2022, July 18.) What Is Revolving Credit and How Can It Ruin Your Credit Score? U.S. News. Retrieved from https://money.usnews.com/credit-cards/articles/what-is-revolving-credit-and-how-can-it-ruin-your-credit-score
- DeNicola, L. (2023, May 19.) 6 ways to lower your credit card utilization. CreditKarma. Retrieved from https://www.creditkarma.com/advice/i/how-to-lower-your-credit-card-utilization
- Segal, T. (2023, April 5.) Revolving Credit vs. Line of Credit: What’s the Difference? Investopedia. Retrieved from https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/110614/what-are-differences-between-revolving-credit-and-line-credit.asp
- Esajian, P. (n.d.) Using A HELOC For Investment Properties Made Simple. FortuneBuilders. Retrieved from https://www.fortunebuilders.com/heloc-on-investment-property/
- Maday, R. (2022, September 14.) How Much Does It Cost to Flip a House? Bob Vila. Retrieved from https://www.bobvila.com/articles/how-much-does-it-cost-to-flip-a-house/
- What is a business line of credit and how does it work? (2022, December 8.) Bank of America. Retrieved from https://www.bankofamerica.com/smallbusiness/resources/post/understanding-business-lines-of-credit/
- Bucci, S. (2021, April 22.) How revolving credit affects your credit score. Bankrate. Retrieved from https://www.bankrate.com/finance/credit-cards/how-revolving-credit-affects-your-credit-score/
- Tuovila, A. (2023, May 24.) What Is Revolving Credit? What It Is, How It Works, and Examples. Investopedia. Retrieved from https://www.investopedia.com/terms/r/revolvingcredit.asp
- What is a Credit Utilization Rate? (n.d.) Experian. Retrieved from https://www.experian.com/blogs/ask-experian/credit-education/score-basics/credit-utilization-rate/