What Are Modular Homes?
Shortcuts
- Modular homes are prefabricated dwellings built in sections in a climate-controlled factory before being trucked to the final site for installation.
- They conform to all relevant local building codes, just like traditional stick-built homes.
- Modular construction can potentially reduce overall costs and speed up build times compared to site-built construction.
- Homebuyers can customize the layout and design features of their modular home.
- While modular homes are movable until installed, they are considered real property once they are permanently affixed to the homeowner’s land.
Understanding Modular Homes
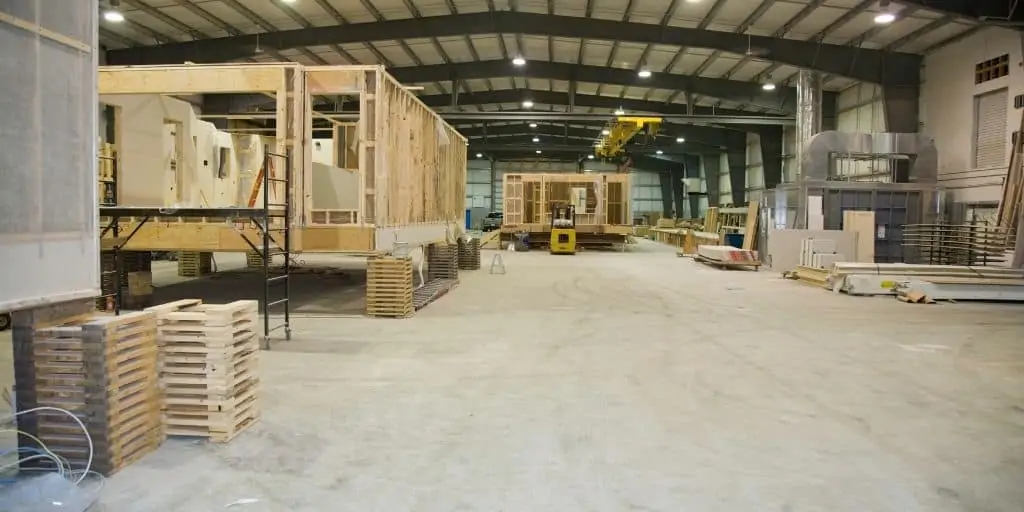
A modular home is a type of prefabricated housing constructed indoors in a factory, similar to a manufactured home.
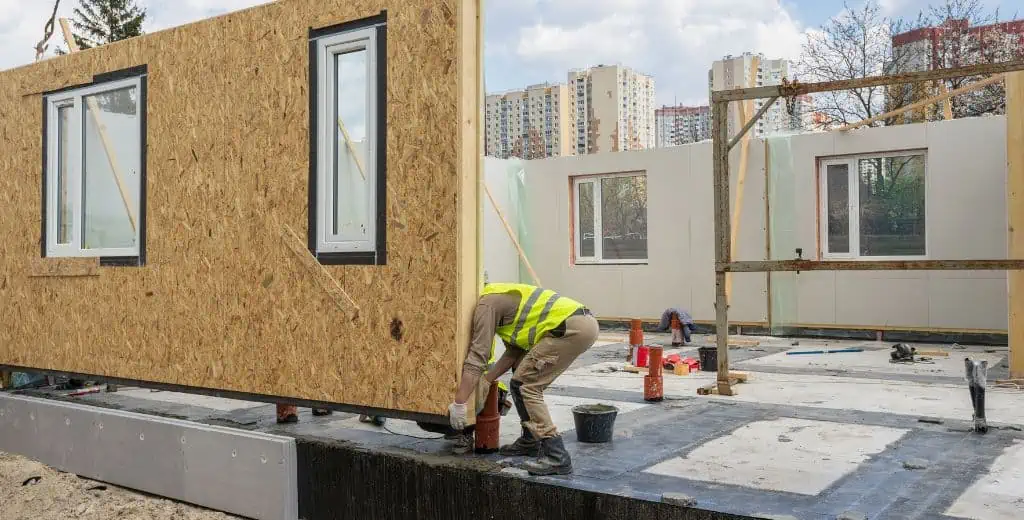
What sets it apart from a manufactured home is that, unlike the latter, which are fabricated as a single unit, modular homes consist of individual sections called “modules.” Once the modules are complete, they are transported to the building location and joined together on a pre-built, permanent foundation.
This makes modular homes similar in appearance to traditional stick-built homes, just built using a different process. They must also comply with all state and local building codes and undergo inspections during various production phases.
Modular homes can be either single-story or multi-story. Single-story modular homes come in mostly the same styles as traditional homes, including Ranch and Cape Cod. Meanwhile, multi-story dwellings are constructed using a specialized stacking process.
How Much Does a Modular Home Cost?
Pricing for modular homes can vary based on square footage, floor plan complexity, interior finishes, location, and other customization choices made by the homebuyer.
Modular home costs per square foot are typically 10% to 20% less than for a comparable site-built home. On average, a homeowner may expect to spend about $270,000 to purchase a new modular home.
Factors influencing a modular home’s final cost include:
- Size and Layout: Larger homes with more complex designs generally cost more, with bedrooms, bathrooms, and specialty rooms adding to the total.
- Interior Finishes: Design choices like flooring, cabinetry, appliances, and fixtures impact pricing.
- Customization Levels: Greater levels of personalization tend to increase costs.
- Land and Site Preparation: The land purchase, site development, foundation work, utility hookups, and any necessary landscaping affect overall project expenses.
- Location: Modular home pricing can vary regionally due to material costs, labor rates, and transportation distances from the factory.
In addition to the upfront costs, owners of modular homes enjoy lower routine maintenance expenses compared to site-built residences. Their factory construction process helps prevent issues common in traditional home building.
Sustainability in Modular Home Construction
Modular construction minimizes material waste. Modular home factories employ precision material cutting, optimizing usage and dramatically reducing jobsite waste compared to traditional framing. Most factories also use recycled or renewable raw materials, like recycled steel or sustainable timber, to construct modules.
In addition, modular homes themselves are more energy-efficient than traditional homes. Modern construction methods for these dwellings include advanced framing techniques and joining processes that create airtight joints and connections, improving overall energy performance. A UK study, for instance, found that it costs 55% less energy to heat a modular home than a traditional brick-and-mortar house.
Finally, because modular homes are constructed in a controlled environment, materials are not exposed to weather that can compromise their integrity. This protects against moisture issues and material degradation.
Leading modular manufacturers pursue third-party green building certifications, such as LEED, ENERGY STAR, and NGBSGreen. Some companies even develop net-zero and passive house modular models attuned to stringent energy standards.
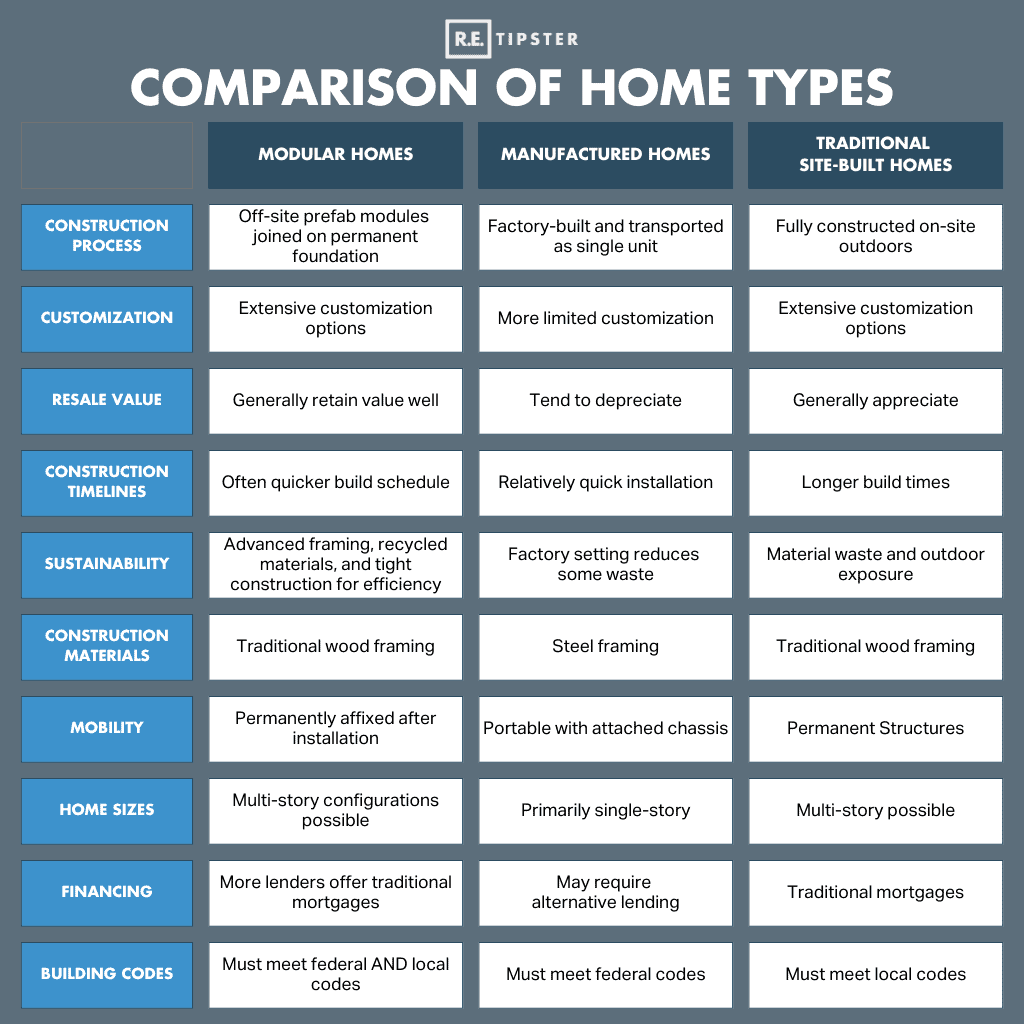
Comparing Modular Homes
When researching housing options, buyers often compare modular homes against manufactured homes and traditional site-built homes. While sharing some overarching similarities, these different home types have distinct characteristics.
Here’s a detailed comparison of these three housing types:
Pros and Cons of Modular Homes
Pros
- Cost Savings: Modular construction can reduce overall building costs compared to traditional site-built methods.
- Faster Build Time: The controlled factory environment allows for a streamlined, predictable schedule, reducing delays common in outdoor construction. On average, modular homes can be built twice as fast as traditional homes.
- Design Flexibility: Just like site-built homes, homebuyers can fully customize their modular home’s layout and features.
- Quality Control: Factory settings provide climate-controlled conditions and specialized tools, contributing to consistent build quality.
- Potential for Green Building: Some modular home manufacturers prioritize sustainable, energy-efficient construction practices.
Cons
- Transport Limitations: Module size restrictions due to over-the-road shipping requirements can impact design possibilities.
- Permanent Installation Required: While movable until installed on a foundation, modular homes cannot be relocated once joined together on their permanent site.
- Zoning Laws: Zoning ordinances or property covenants in some communities restrict or prohibit the placement of modular homes. Most modular homeowners need to own the land where the home’s foundation is installed or purchase that land beforehand.
- Lender Requirements: Securing traditional home loans can be more complex for modular construction until the home is permanently installed and valued.
Frequently Asked Questions: Modular Homes
Are modular homes built to the same codes as site-built homes?
Yes, modular homes adhere to all relevant state and local building codes, ensuring equivalent quality and safety standards as traditional stick-built residences.
The modules undergo specific third-party inspections and certifications during the factory construction phase to verify they meet building code requirements before being transported.
Do modular homes retain their value like traditional homes?
Yes, modular homes retain their value similarly to traditional homes. They are usually counted the same as regular homes in terms of value and thus don’t depreciate as long as they are well-maintained and located in a desirable area.
Factors such as location, condition, and unique features can influence the resale value of modular homes, making them a sound investment choice that appreciates over time.
Can modular homes be customized?
Absolutely. Modular homes offer extensive customization options similar to a traditional home build. Homebuyers work alongside the builder to design their ideal layout, handpick interior and exterior finishes, and include any desired specialty rooms or features that fit their lifestyle needs and budget.
Some modular manufacturers further cater to luxury buyers by allowing greater architectural expression and high-end material selections for those seeking distinct, upscale living environments.