What Is an SBA 504 Loan?
REtipster does not provide tax, investment, or financial advice. Always seek the help of a licensed financial professional before taking action.
Overview of the SBA 504 Loan Program
An SBA 504 loan provides funding assistance to finance the acquisition and improvement of major business assets, such as real estate, equipment, and fixtures, plus other professional fees and interest expenses incurred in the process.
The SBA 504 loan is named after Section 504 of the Small Business Investment Act of 1958[1]. One of its goals is to encourage lenders to finance businesses that are otherwise considered too great a risk, either because they are a new business or in a higher-risk industry. This goal aligns with the SBA’s underlying motivation to enhance business growth and create jobs.
Under this program, qualified borrowers may obtain loan amounts of up to $5 million for up to 20 years for real estate and 10 years for equipment[2]. In some cases, eligible energy-efficient or manufacturing projects may obtain up to $5.5 million each[3].
The SBA 504 loan program also appeals to borrowers because of the lower down payment (as low as 10%) and the 20-year fixed rate on the 504 loan (10-year fixed rate on equipment projects). How low the down payment is depends on the borrower’s experience and the assets being financed. Because of these reasons, the SBA 504 loan is popular among small business owners.
Note that the SBA 504 program is not designed only for the riskiest credit but also as a tool for third-party lenders to mitigate risk for their entire portfolio. Both weak and strong borrowers can utilize the SBA 504 loan program.
How a Typical SBA 504 Loan Is Processed
Every SBA 504 loan is administered through a partnership between the Small Business Administration and a Certified Development Company (CDC). CDCs are non-profit organizations that the SBA has authorized to “package, process, close, and service 504 loans[4].”
In turn, the CDCs (on behalf of the SBA) work in conjunction with a third-party lender, like a bank or credit union that provides an interim loan, to fund the majority of the project. When this initial funding is complete and all costs have been verified, the SBA loan is closed and funded, reducing the bank’s loan balance, usually down to 50% of the original project amount.
After SBA funding, the third-party lender remains in first lien position on all project assets while the SBA is in second lien position. This first lien position at only 50% LTV is an attractive benefit for banks and credit unions who want to mitigate the overall risk of their loan portfolio.
How the SBA and CDCs Work Together in Every 504 Loan
In a sense, the SBA delegates much of the work of finding, originating, approving, closing, and servicing each 504 loan to a CDC.
While a CDC is tasked with performing the bulk of the work for each 504 project, each loan still needs to be approved by SBA in the beginning. When the SBA has reviewed and approved the application and supporting documentation collected from the borrower and submitted by the CDC, an SBA Authorization will be issued. The Authorization effectively spells out all the terms and conditions that need to be fulfilled for the SBA to fund the 504 portion of the project.
A representative of the CDC will work with the borrower and third-party lender to obtain SBA approval. This representative will stay in touch with all parties until the SBA 504 loan is closed and funded. In addition, because a 504 loan is an actual loan—not a guarantee, like the SBA 7(a) loan program—a representative will also stay involved to provide servicing requests for the duration of the 504 loan.
The National Association of Development Companies (NADCO) is the trade association that represents over 200 CDCs across the U.S.[5] There are approximately 270 CDCs nationwide, with each CDC covering a specific geographic area.
Pros and Cons of the SBA 504 Loan Program
There are a few major benefits of using the SBA 504 loan program, for both the bank and the borrower, but there are some trade-offs to consider as well.
Pros of the SBA 504 Loan Program
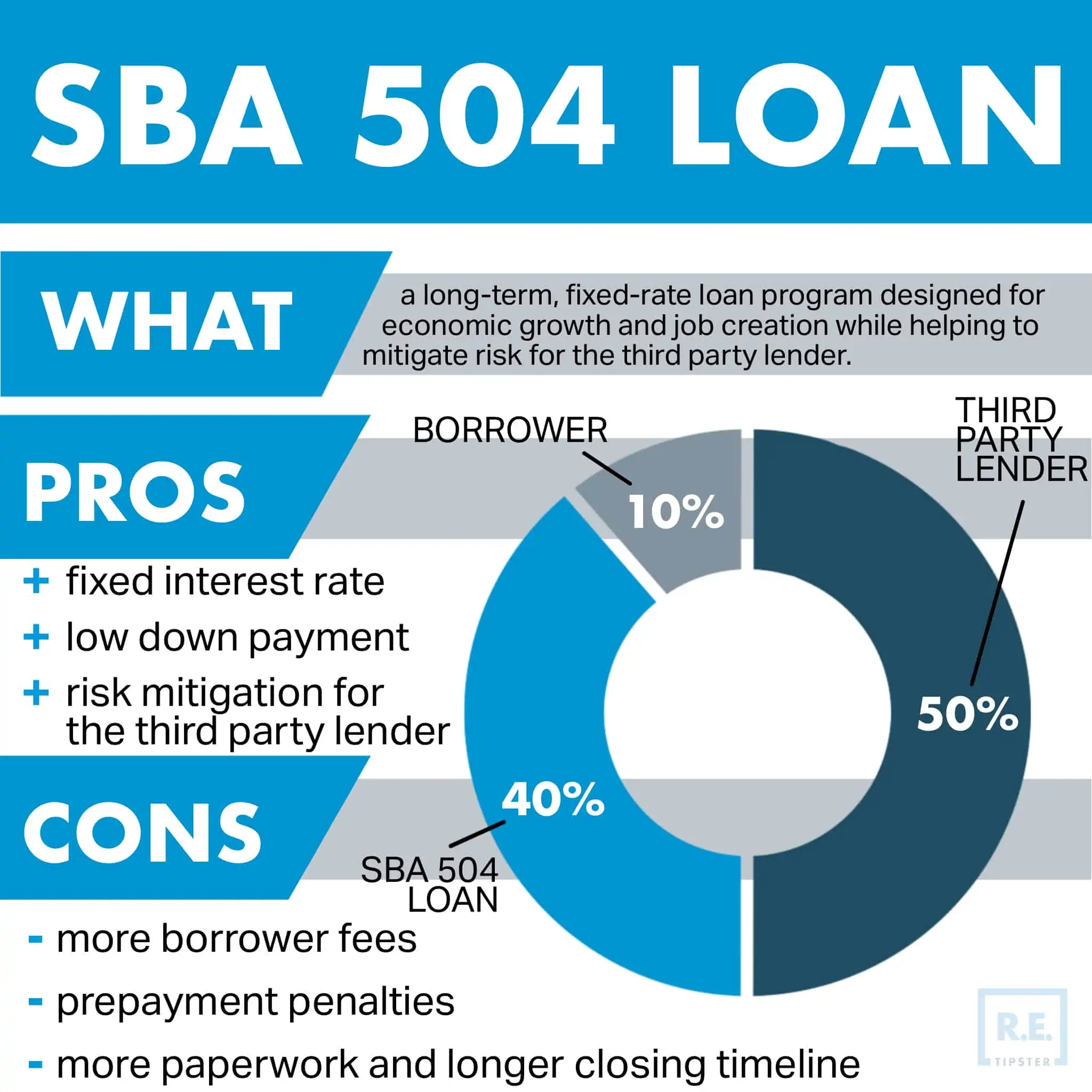
- Fixed interest. While most traditional commercial loans are designed to amortize over 10 to 20 years with an interest rate that adjusts every five to seven years, a 504 loan has a fixed rate that will not change for the entire duration. This kind of fixed interest rate gives the borrower better stability and predictability in knowing what their payment will be for the full duration of the payback period on the SBA 504 portion of their loan.
- Low down payment. A typical SBA 504 project follows the 50/40/10 structure, where a bank contributes 50%, the SBA contributes 40%, and the borrower contributes 10%. This setup features a significantly lower down payment compared to a typical commercial loan, which can require a 20% to 30% contribution from the borrower.
- Less LTV. Perhaps the biggest benefit for the third-party lender is that after the 504 loan has been funded, they will have a 50% loan-to-value (LTV). Even though the bank has only advanced 50% of the project proceeds, they will be in first lien position on all the project assets, while SBA will be in second position. This eliminates a huge amount of the bank’s risk by having first access to the project collateral.
Compared to a traditional loan, where the bank would be at 70% to 80% loan-to-value, the 504 loan program allows the third-party lender to get far more comfortable with borrowers because of this extra security.
Cons of the SBA 504 Loan Program
- More paperwork. With the SBA 504 loan program, the borrower is splitting their debt into two separate loans, instead of one loan to their bank. This means they will have run through most of the approval and closing process twice (two loan applications, two loan approvals, two loan closings, two title insurance policies, etc). The borrower will also have a long-term relationship with two lenders—the bank and the CDC they chose to work with on their SBA 504 loan.
- More fees. With two loans involved, the borrower will have to pay additional fees that are not normally required in a conventional loan scenario. Luckily, all of the fees are effectively rolled into the SBA loan amount and/or paid in monthly increments as the loan balance is paid down.
If the borrower’s priority is to keep their injection as low as possible and get a fixed interest rate, then the benefit of a 504 loan will likely outweigh these additional costs. However, if minimizing fees and paperwork is a borrower’s primary concern, the SBA may not be the borrower’s first preference unless the bank requires the SBA’s support to finance the project.
- Longer timeline. In a traditional loan scenario, the bank will typically fund and close on the deal as soon as the loan is underwritten and approved internally and the appraisal is reviewed and approved. However, with an SBA 504 loan, the bank will not be able to close their initial loan until their internal department, and the CDC/SBA has reviewed and approved all the same information, along with additional application forms required by the SBA. In most cases, this results in a longer timeline for the borrower to close with the bank and purchase their assets.
Similarly, note that the SBA 504 loan cannot close and fund until after the bank has fully funded the project costs and the CDC can verify all the costs.
When buying a single piece of equipment or a building purchase, this cost verification process is relatively quick and simple. However, in the case of constructing a new building or buying hundreds of pieces of equipment, it will take many months (even years) to complete the process and verify the costs before the SBA can close and fund their portion of the project. The 504 loan rate will not be fixed until this funding date, which can create uncertainty about where the rate will end up between the time of approval and funding.
- Prepayment penalty/ies. Because 504 loans are funded through a debenture pegged to an increment above the current market rate for 5- and 10-year U.S. Treasury issues[2], the investors who buy these U.S. Treasury Bonds are given a guaranteed rate of return based on the assumption that the borrower continues paying their monthly payment as planned.
Suppose a borrower wants to sell their real estate or equipment before the end of their loan amortization and pay off their loan. They can only prepay the loan in full, and there is a prepayment penalty applied for the first half of the payback period for 504 loans (the first ten years for a 20-year debenture and the first five years for a 10-year debenture). This prepayment penalty declines yearly and goes away entirely after the first half of the amortization period.
The prepayment penalty starts at 3% of the loan balance in year one and declines each consecutive year until it hits 0% in the 11th year and beyond until the loan is paid in full.
The chart below shows how the prepayment penalty lowers over the life of the loan. Note that the percentage varies based on the debenture rate for the loan[6].
| Year | Prepayment Amount (% of the loan balance) |
| 1 | 3.00% |
| 2 | 2.70% |
| 3 | 2.40% |
| 4 | 2.10% |
| 5 | 1.80% |
| 6 | 1.50% |
| 7 | 1.20% |
| 8 | 0.90% |
| 9 | 0.60% |
| 10 | 0.30% |
| 11-20 | 0.00% |
SBA loans are not the only type of commercial loan that requires a prepayment penalty. It may also be possible for a 504 loan to be assumed by a new buyer, provided that their business can also qualify for the SBA 504 loan program by all the same standards as the original borrower. This is another potential drawback or limitation that borrowers should consider before committing to the 504 loan program.
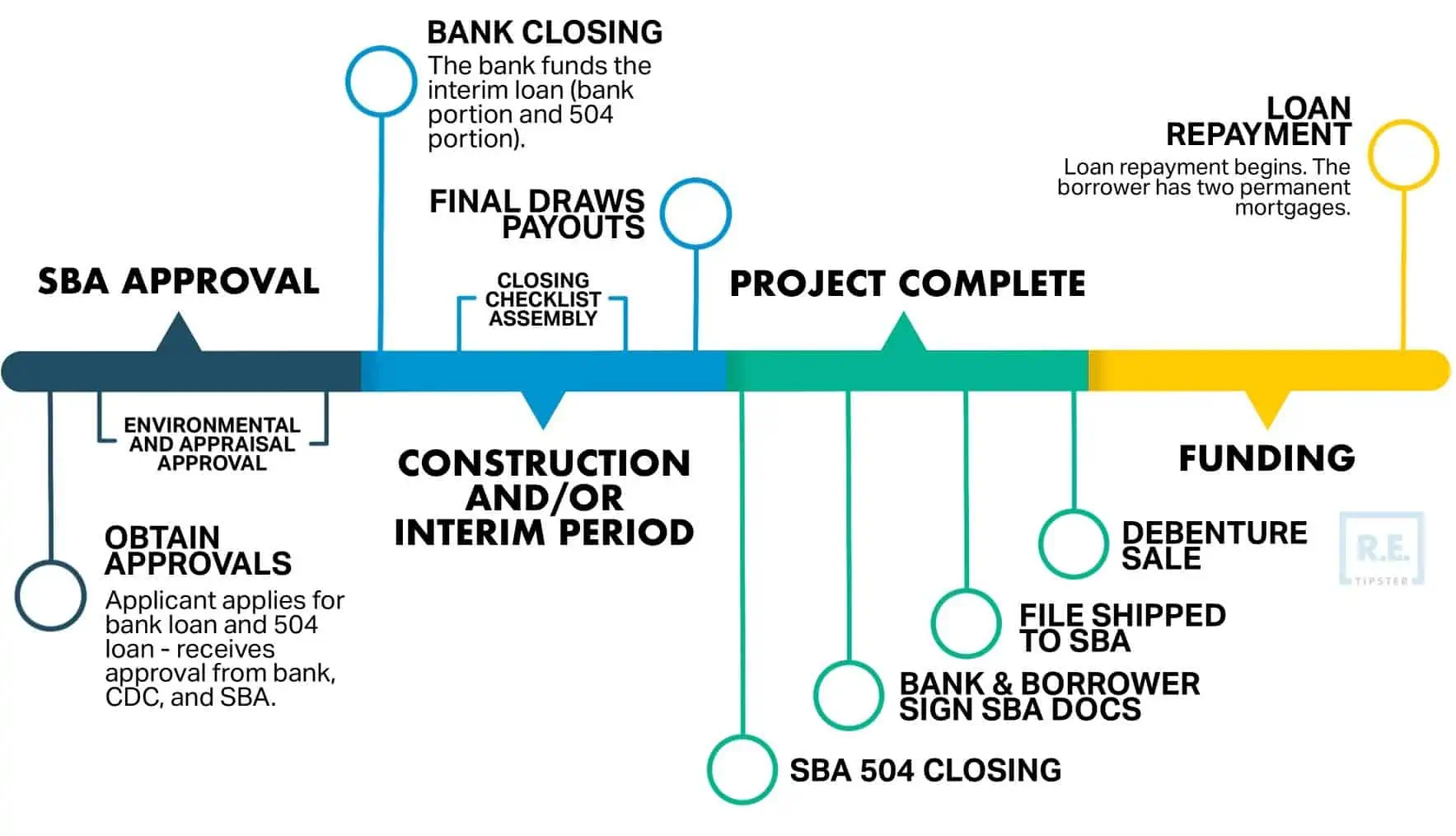
SBA 504 Approval and Funding Timeline
Every 504 loan project starts with a bank and a borrower who want to do business together, and both parties want to engage the help of SBA to provide the benefits to both parties.
When a CDC has been chosen (typically selected by the bank), the CDC will work with the bank and borrower to collect the needed information and submit 504 loan application to SBA.
When SBA has reviewed and approved the 504 loan, SBA will issue its Authorization, which outlines all the terms and conditions of the 504 loan and provides the information needed for the bank to then proceed with funding both the bank’s 50% portion and SBA’s 40% portion of the loan.
During this interim period, the bank has advanced all of the project proceeds and is at 90% LTV while the borrower is working to acquire the project assets. In some cases, this is as simple as purchasing an existing building or piece of equipment, which may only take a month or two to complete. In other cases, this may involve constructing a new building, which can take years.
In either case, the CDC cannot close the loan and SBA cannot fund the 504 portion of the project until the bank has fully advanced all the loan proceeds and all the assets have been purchased or constructed. These costs need to be verified by the CDC prior to closing.
Once the conditions of the SBA Authorization are fulfilled (construction and/or acquisition of the project assets is completed with all documentation gathered and verified), a representative from the CDC will meet with the third-party lender and borrower to sign closing documents.
The completed documents are then submitted to the SBA by the CDC’s closing attorney, and the debenture is typically funded six to eight weeks later. At the time of funding, the SBA’s portion of the project is wired directly to the third-party lender to pay down their interim loan, which lowers their outstanding loan amount to 50% of the total project cost.
At the time of funding, the fully effective interest rate is locked in for the duration of the 504 loan. Depending on the type of project, this can be from 10 years for equipment loans and up to 20 years for real estate loans.
How Is an SBA 504 Loan Structured?
The SBA 504 loan structure varies depending on several factors, such as the business type, the borrower’s experience (new or existing business), the total project cost, the type of assets being financed, and more.
Three distinct parties participate in every SBA 504 loan:
- Third-party lender — In most cases, the third party lender is a bank or credit union. They will contribute up to 50% of the total loan amount.
- SBA — The SBA can contribute up to 40% of the total project amount.
- Borrower — The borrower puts up the remaining difference not covered by the third-party lender or SBA. In most cases, the amount is 10% of the total project cost, but it could be more if the borrower is a new business or if the real estate is a special-use building.
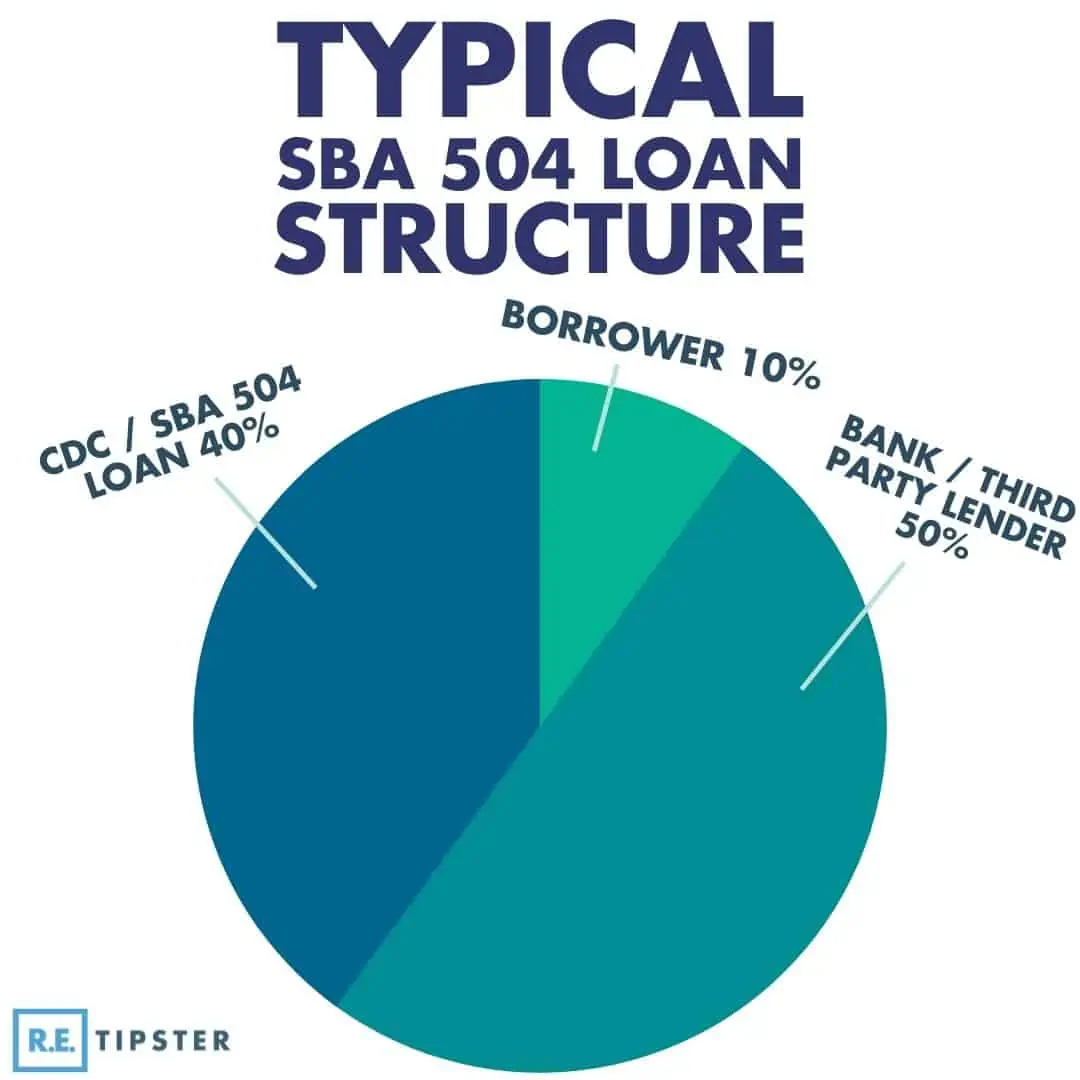
Most SBA 504 loans follow a 50-40-10 structure. For instance, in a $1 million project, the funding sources are broken down as follows:
- Third-party lender: $500,000 (50%)
- SBA 504: $400,000 (40%)
- Borrower: $100,000 (10%)
- TOTAL: $1,000,000 (100%)
At the initial funding, the third-party lender (TPL) will advance $900,000 to cover both the TPL and the SBA portion. This can be advanced as a single interim loan for $900,000 that require interest-only payments until the date of SBA funding.
Alternatively, it could be advanced as two separate loans, one for $500,000 and another for $400,000. The advantage of advancing two separate loans is that the bank can begin amortizing its 50% loan sooner rather than later. Whereas with one loan covering both loan amounts, the bank cannot term out their loan until the SBA funds their portion.
Exceptions to the 50-40-10 Structure
Under certain circumstances, for example, if the business is new or the purpose of the loan is to finance special purpose real estate[7], the SBA may require a 15% or even 20% down payment. Such a requirement may effectively change the structure to 50/35/15 or 50/30/20, respectively.
In other cases, if the project is so large that 40% exceeds SBA’s limit of $5 million, a project can be structured in whatever way the bank and borrower could maximize the SBA loan amount, as long as the bank’s portion is not lower than SBA’s contribution and the remainder is covered by a combination of bank and borrower contributions.
For example, if the total project cost is $20 million and the borrower still meets the eligibility requirements of a small business[2], the loan may be structured 60/25/15, as follows:
- Third-party lender: $12,000,000 (60%)
- SBA 504: $5,000,000 (25%)
- Borrower: $3,000,000 (15%)
- TOTAL: $20,000,000 (100%)
In addition, it is possible for the third-party loan amount to exceed 50%, so long as the borrower contributes at least 10%.
Conversely, it is also possible for the third-party loan amount to be less than 50%. The bank’s loan amount may even match the SBA loan amount, provided the SBA loan amount does not exceed 40% of the total project cost. Likewise, the SBA contribution can never exceed the third-party lender’s contribution.
Interest Rates
SBA 504 interest rates are typically based on the current market rate for the 5- and 10-year U.S. Treasury notes, amounting to around 3% of the loan amount[8]. When interest rates for 504 debentures are advertised by a CDC, they are advertised at the “fully effective rate,” which includes all of the monthly servicing fees as required with every 504 loan.
While a long-term fixed rate is one of the big advantages of a 504 loan, this rate is not locked in until the 504 loan is closed and funded. This phase typically happens over several months, sometimes even years after the bank advances the initial loan to fund the purchase or construction of the project assets.
Fees
SBA 504 loans require additional fees that are rolled into the loan amount and paid off over the term of the loan (so the borrower does not need to pay these fees upfront).
The standard fees listed in every SBA Authorization are as follows:
- SBA Guarantee Fee: 0.5% of SBA Debenture Proceeds (SBA Contribution x 0.005)
- Funding Fee: 0.25% of SBA Debenture Proceeds (SBA Contribution x 0.0025)
- CDC Processing Fee: 1.5% of SBA Debenture Proceeds (SBA Contribution x 0.015)
- CDC Closing Fee: Not to exceed $2,500
- Underwriter’s Fee: For 20-year debentures, the sum of the SBA Contribution plus all closing costs divided by 0.996 rounded up to the next higher thousand, multiplied by 0.004. For 10-year Debentures, the sum of the SBA Contribution plus all closing costs, divided by 0.99625, rounded up to the next highest thousand, multiplied by 0.00375.
- Third-Party Lender Fee: While this fee is technically paid by the bank, nearly every bank will pass this cost onto the borrower and require them to pay it upfront. This fee is equal to one-half percent (0.5%) of the principal amount of the bank’s senior loan amount.
Additionally, there are monthly servicing fees included in the effective interest rate and defaulted in the monthly payment amount for the life of the 504 loan. These fees are paid to the SBA (0.368%), the CDC (0.625%) and the Central Servicing Agent or CSA (0.1%). These fees are determined by the initial gross debenture loan amount and are reduced at five-year intervals when they are recalculated based on the lower loan balance.
Term
The term refers to how long the borrower has to repay the loan. Repayments on 504 loan programs are withdrawn automatically each month by the CSA and include all of the monthly servicing fees detailed above.
Term lengths vary depending on the primary purpose of the loan. For real estate purchases, the loan term is 20 years while loans for machinery and long-term equipment typically have a term length of 10 years.
SBA 504 Loan Eligibility Requirements
Under the SBA 504 program, there are numerous eligibility requirements[9] for borrowers, lenders, and what the project proceeds can be spent on.
Borrower Eligibility
Since 504 loans are designed for borrowers requiring business funding assistance, business owners with easy access to other low-interest loans may be ineligible.
Other requirements include:
- The business must be worth at most $15 million.
- The business must be a for-profit entity in the United States.
- The business must have an average net income of no more than $5 million after federal income taxes for the two years before the loan application.
- Businesses that engage in passive or speculative activities are ineligible.
- The business must meet certain job creation requirements (since job creation is one of the primary goals behind the 504 loan program). Alternatively, the business must meet its community’s economic development or public policy goals.
- The business owner must be creditworthy and not have any loan defaults in the past. Any past default on an SBA loan will make the application ineligible.
- The business must meet other general SBA loan eligibility standards, including having a feasible business plan, qualified management expertise, and the ability to repay the loan.
- 504 loans are not intended to finance investment real estate (borrowers who buy real estate that they are not planning to occupy). In some cases, a borrower can lease out some of the excess space in their building as long as they are occupying at least 51% of the space.
In the case of new construction, the borrower must occupy at least 60% of the building with the plan of occupying 80% of the property within the next ten years[10].
Lender Eligibility
Requirements include:
- The company must meet the minimum lending activity level requirements.
- The company must have a full-time, professional management team overseeing its operations and a board of directors.
- The company must be an SBA-approved lender.
Project Eligibility
Project eligibility involves meeting the usage requirements of the loan. These include:
- The loan must be used to fund projects that create jobs or meet community development goals. For every $65,000 approved, the business must hire or retain one job[11].
- Borrowers cannot use the loan to purchase and hold real estate. Any land or properties bought with the loan must be used to tackle long-term business needs. If the property is an existing structure, the business owner must plan to occupy at least 51% of the building. For new constructions, the occupancy rate must be at least 61%[12].
- The loan cannot be lent out to other borrowers.
- The loan cannot be used for political or lobbying activity.
- The loan cannot be used to fund the business’s working capital or inventory nor can it be used to consolidate or repay debt.
- Repayment of the loan must come from the cash flow generated by the project for which it was approved.
How to Apply for an SBA 504 Loan
To apply for an SBA 504 loan, qualified borrowers must first have a bank or credit union willing to participate as the Third Party Lender for the project. The loan applicant can apply for an SBA 504 loan either after the third-party lender has approved their loan or simultaneously during the bank’s approval process.
Unlike the SBA 7(a) loan program, all SBA 504 loan application must go through a CDC.
The first step is to find a CDC that serves the market where the project is located and ensure that the CDC is an SBA-certified lender.
Borrowers may visit the SBA website to find a CDC In their area.
After the bank and borrower choose and contact a CDC, the CDC can instruct them on the next steps required to prepare and submit the relevant documents. The typical application documents are similar to what a bank or credit union will ask for, but many of them must be completed on SBA-specific forms.
The standard checklist includes (but is not limited to):
- Tax returns of the business and its owner for the last three years.
- Year-to-Date and Interim financial statements of the business (credit score, accounts payable and receivable, income statement, balance sheet, debt schedule, etc.).
- Viable and detailed business plan.
- Various SBA application forms, including a statement of personal history (SBA Form 912) and personal financial statement (SBA Form 413), among others.
- Statement of intent and plan for how the loan will be used (cost documentation, contractor estimates, etc.).
The CDC and the lender may require additional documentation before processing the 504 loan application.
The full SBA 504 application form can be downloaded here.
Applications can take anywhere from one to three months to be approved, possibly longer if the SBA underwriters require more information while reviewing the project.
Once the SBA 504 application is approved and the bank has advanced its funds, the closing timeline for the 504 loans can take months to years, depending on the complexity of the project and how long it takes to purchase and/or construct all the project assets. Not surprisingly, loan applications for larger and more complex projects typically take longer to approve and close.
Common Misunderstandings and Points of Confusion About SBA 504 Loans
Since there is more than one type of SBA loan product, it is not uncommon for banks and borrowers to misunderstand exactly what type of borrower a 504 loan is designed for and how it works.
Here are a few of the common scenarios or issues that can cause confusion for banks and borrowers.
When the Rate Is Fixed
The interest rate is not locked in until the date of funding. This does not occur until all the following events have transpired:
- After SBA has issued the Authorization.
- The third-party lender has funded the interim loan.
- The CDC has verified that all project proceeds have been spent according to plan.
- The CDC has closed the 504 portion of the loan and has submitted it to the SBA for funding.
Depending on the complexity of the project and what is involved, this process may take anywhere from a few months to a few years, though most 504 loans are funded within 12 months.
Fully Effective Rate vs. Actual Rate
When a borrower makes their 504 loan payments, there are a few monthly fees included in every payment. When these fees are included with the payment amount, the CDC will quote the borrower’s “fully effective rate.”
If these fees are not included, their rate will be substantially lower. Since these fees are not optional, the rate quoted is always the fully effective rate.
No Adverse Change
One of the many conditions listed in the SBA Authorization is that there must not be “no unremedied substantial adverse change” to the business since the date of application. The CDC is required to review the borrower’s current financials and verify that their performance is sufficiently strong prior to submitting the 504 loan for funding.
If the business is not performing according to its pro forma and does not have sufficient cash flow coverage to pay its interest-only interim loan payment, it will be in an even worse position after the SBA loan funds, because the monthly payment will increase to include the principal and interest after funding.
In situations where a business has experienced an adverse change, this presents an obvious problem for the third-party lender, who has advanced up to 90% of the project proceeds for a borrower that is unable to show sufficient cash flow. Understandably, the bank will want their SBA paydown as soon as possible to shore up their position, but SBA will not fund the debenture if the borrower is unable to make their payments. This situation often creates a strain on the relationship between the bank and the CDC, because the bank is left holding the risk without the loan payoff it had planned for.
For this reason, it is important that all parties work together to close the 504 loan as quickly as possible and eliminate unnecessary delays when funding it, which only adds to the uncertainty of the borrower’s future performance.
Meanwhile, third-party lenders should carefully consider this risk during their approval process. While the situation is uncommon and unlikely, it is a possibility. As such, the bank should consider the risk of lending to a business that may not perform according to its projections, and not merely use SBA because the borrower represents a higher-than-normal risk for the bank.
Takeaways
- SBA 504 loans provide small businesses with long-term, fixed-rate financing of up to $5 million. These loans are primarily for job creation, business growth promotion, and meeting economic development goals in the community.
- Qualified borrowers may use the loan amount to purchase land, buildings, machinery, furniture, fixtures, and long-term equipment.
- All applications for SBA 504 loans must be made through a CDC operating in the borrower’s community.
- SBA 504 loans offer the advantage of a 20-year fixed-rate interest, a lower down payment for borrowers, and significant risk mitigation for lenders.
Sources
- Martin, W., Moore, R. (1959). The Small Business Investment Act of 1958. California Law Review, 47(1), 144–170. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.2307/3478778
- Small Business Administration. (n.d.) 504 loans. Retrieved from https://www.sba.gov/funding-programs/loans/504-loans
- Small Business Administration. (n.d.) 504 Loan Fact Sheet. Retrieved from https://www.sba.gov/brand/assets/sba/sba-lenders/504-Loan-Fact-Sheet-Borrower-Version.pdf
- Office of Financial Assistance. (n.d.) CDC Certification Guide. Small Business Administration. Retrieved from https://www.sba.gov/document/support–cdc-certification-guide
- National Association of Development Companies. (n.d.) The SBA 504 Loan. Retrieved from https://www.nadco.org/mpage/504lenders
- SBA504.LOANS. (2018.) Are There Prepayment Penalties with an SBA 504 Loan? Retrieved from https://sba504.loans/sba-504-blog/prepayment-penalties-and-sba-504-loans
- TMC Financing. (n.d.) SBA 504 Single Purpose Property List. Retrieved from https://www.tmcfinancing.com/sba-504-loans/sba-single-purpose-property-list/
- Williams, R. (2022.) What Are Current SBA Loan Rates in 2022? ValuePenguin. Retrieved from https://www.valuepenguin.com/small-business/sba-loan-rates
- SBA504.Loans. (n.d.) Loan Requirements for Borrowers, Projects, Lenders, and More. Retrieved from https://sba504.loans/loan-requirements
- Small Business Administration. (2017.) The SBA 504 Loan Program. Retrieved from https://www.sba.gov/sites/default/files/articles/SBA_504_Presentation_-_March_21_2017.pdf
- Southeast Texas Economic Development Foundation. (n.d.) Why Choose an SBA 504 Loan? Retrieved from https://www.setedf.org/why-choose-an-sba-504-loan.aspx
- Working Capital. (2020.) What is an SBA 504 Loan and How Can You Apply? FORA Financial. Retrieved from https://www.forafinancial.com/blog/working-capital/sba-504-loan/