1031 Exchange Definition
REtipster does not provide tax, investment, or financial advice. Always seek the help of a licensed financial professional before taking action.
What is a 1031 Exchange?
In a 1031 exchange, an investor changes the form of his investment without cashing out or incurring a capital gains tax liability. There is no limit to the number of times an investor can realize a profit through a 1031 exchange. The capital gains tax only applies when the investor ultimately cashes out.
The 1031 exchange only applies to investment and business property; taxpayers are not allowed to swap one personal residence for another under the law. There is, however, a loophole that can be used for vacation properties in certain circumstances.
A common misconception is that in a 1031 like-kind exchange, the properties must be similar in nature (i.e., one duplex for another or one office building for another). However, “like-kind” in this context means only that the investments in the exchange are both real property. In other words, an investor cannot use a 1031 exchange to swap an airplane for a franchise license, for example, but he could swap a restaurant building for a vacation rental.
Why Consider a 1031 Exchange?
Although the rules for a 1031 exchange are quite specific, it is actually a flexible tax-deferral vehicle. These are just a few scenarios in which an investor might consider using a 1031 exchange:
- To capture profit in an appreciating market: If an investor owns property that is rapidly increasing in value, they could use a 1031 exchange to lock in profits at the higher price point without liquidating the investment or paying capital gains.
- To diversify an investment portfolio: An investor who owns apartment complexes in California can use a 1031 exchange to acquire single-family rental homes in Nevada.
- To accomplish estate planning goals: An investor with four heirs who owns a single income-producing property can use a 1031 exchange to swap it for four equally valued tenancy-in-common (TIC) interests in a real estate investment. The heirs need not jointly decide whether to sell or hold the building because each heir now receives a TIC interest with a stepped-up basis, which they can hold or sell as they prefer.
- To resolve tenant, management, or maintenance issues: An investor can use a 1031 exchange to get out of a troublesome investment.
- To leverage deferred gains: An investor with significant gains can use a 1031 exchange to acquire a significantly more valuable property while deferring any capital gains tax liability.
- To increase cash flow: An investor who owns a single-family rental can use a 1031 exchange to trade up to a multi-unit property with stronger monthly cash flow.
- To defer or potentially eliminate taxes on gains: Capital gains taxes are not triggered until the asset is ultimately sold for cash, which means they can be deferred indefinitely using a 1031 exchange. In addition, when the investor dies, heirs inherit the property with a stepped-up basis, in essence forgiving the gain.
How a 1031 Exchange Works
Depending on the situation, there are four types of 1031 exchanges investors may use.
Delayed 1031 Exchange
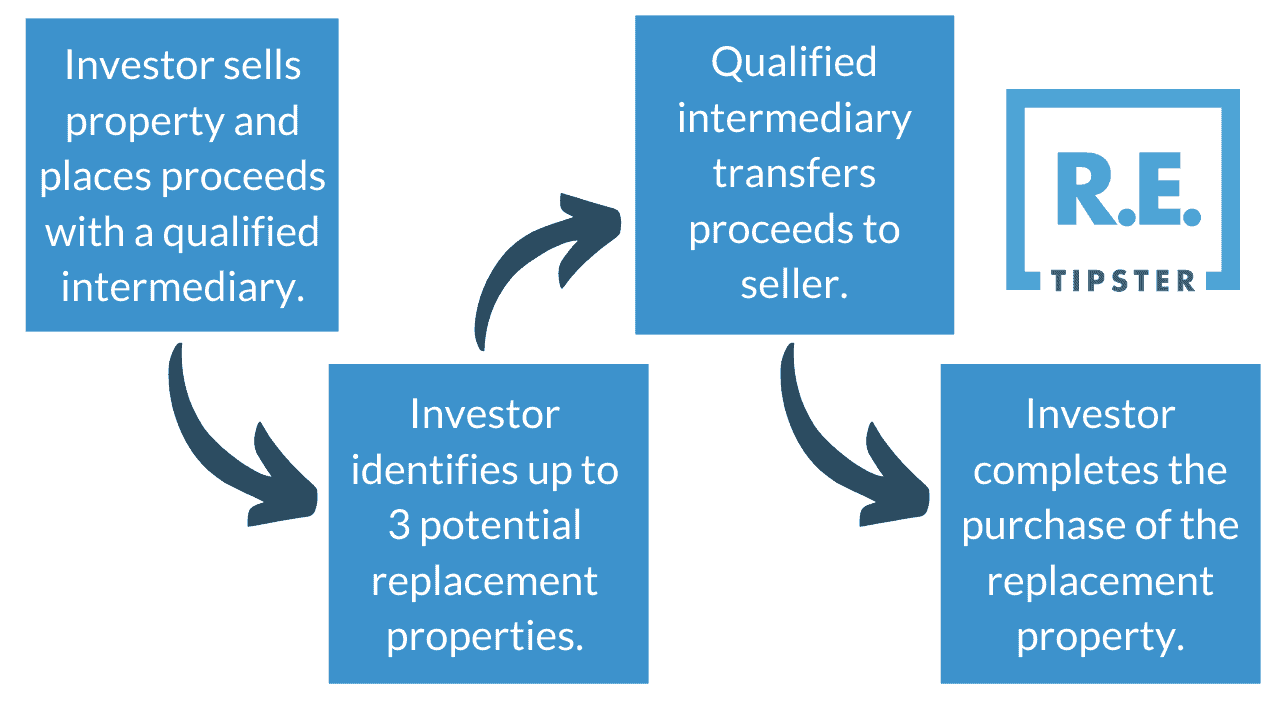
This is the most common type of 1031 exchange. In this scenario, the investor sells the property to be exchanged and places the proceeds with a qualified intermediary. They have 45 days from the date of the sale to identify a replacement property and 180 days to complete the deal.
Simultaneous 1031 Exchange
In a simultaneous exchange, both transactions close on the same day. This is typically accomplished by the two parties swapping deeds or using a qualified intermediary who structures the transactions to occur simultaneously. In a simultaneous exchange, it is essential that both transactions close at the same time; even a delay of a single day can trigger capital gains taxes.
Reverse or Forward 1031 Exchange
In this exchange, the investor buys the property first and then selects which of their owned properties will be relinquished in the exchange. The investor has 45 days from the date of purchase to identify the property to be sold and 180 days to complete the sale. This exchange requires the use of an exchange accommodation titleholder to hold legal title to the property until it can be conveyed to the buyer.
RELATED: What is a Reverse 1031 Exchange?
Construction 1031 Exchange
In a construction or “build-to-suit” exchange, investors can use the proceeds from a 1031 exchange to build or substantially improve a property. This exchange requires an exchange accommodation titleholder to purchase and hold the replacement property until construction is complete and the investor can officially take the title.
Depreciation Recapture in 1031 Exchanges
Special tax rules apply when a depreciable property is used in a 1031 exchange. When a property is sold, capital gains tax is calculated on its net-adjusted basis, which is the original purchase price and any capital improvements less depreciation. Depreciation is thus taxable income if the property’s sales price is higher than its net-adjusted basis.
Depreciation recapture is a variable that investors must consider when calculating the potential costs and value of a 1031 exchange. This recapture can be rolled into the replacement property and deferred until the property is sold, but it must be tracked and accounted for in the eventual cash-out.
1031 Exchange Rules to Keep in Mind
- The definition of “like-kind” property is fairly broad as long as the property in question is business or income-producing real estate located in the United States. “Like-kind” also doesn’t require an equal number of properties to be exchanged, i.e., an investor could swap one apartment complex for 10 single-family rental properties.
- The 1031 exchange is for a business or investment property only. A taxpayer cannot use the law to swap one primary residence for another primary residence or vacation home.
- Both market value and equity must be the same or greater in the exchanged property. For example, if an investor is relinquishing a property valued at $1 million with a $500,000 mortgage, the new property must be valued at $1 million or more and the investor will have to carry a mortgage of at least $500,000 on the new property. If the new property is of less value, the difference is known as a “boot,” and is taxable at the normal capital gains tax rate.
- The same taxpayer must appear on both the title of the new property and the tax return reporting the exchange. There is an exception for a single-member LLC, however. The LLC can sell the property and the single-member can buy the new property without triggering a 1031 compliance violation.
- Investors must adhere to the timing of both the identification of replacement properties and the date of the transaction closing. The 45- and 180-day countdowns run simultaneously, which means the entire deal must be completed within 180 days of the date of sale of the relinquished property.
RELATED: TAX HACKS: Doing a 1031 Exchange (the Easy Way) with RealtyMogul